
Choosing the right custom label printing method can be hard for businesses. The best method depends on your budget, how many labels you need, and how you want each label to look. The price for each label changes with the printing method and how many you order. You can see this in the table below:
Run Size | Printing Method | Cost Characteristics and Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Small | Digital Printing | Best value for each label, no extra tool costs, lots of choices |
Medium | Digital or Hybrid | Cheaper for many SKUs, good for different label types |
Large | Flexographic Printing | Saves the most money, prints fast, great for big orders |
Thermal labels are important for quick and strong label printing in stores and shipping. This guide helps you look at your options and pick the best label for what you need.
Key Takeaways
Pick your label printing method by thinking about your budget, how many labels you need, and your design needs. This helps you get good value and quality. Digital printing is best for small or medium orders. It is good if you want to change designs often. It is also fast. Flexographic and gravure printing save money if you order a lot of labels. They take more time to set up. They work best if you use the same design many times. Screen and rotary screen printing make strong and tough labels. These labels are good for outdoor or factory use. Choose a label printing company that lets you change designs, gives you good samples, works fast, and follows industry rules.
Custom Label Printing Methods

Picking the right custom label printing method depends on your product, budget, and design needs. Every method has its own strengths for different label and sticker projects. You can read below to learn about each method, how it works, what it is best for, and some technical details.
Digital Printing
Digital printing uses digital files to print images straight onto label materials. This method does not need printing plates or screens.
Definition: Digital printing makes labels by moving digital images right onto the material. It is fast and flexible.
Process: The operator puts the design file into the printer. They set up cutting and finishing choices. Then, they send the job to print. Special software helps with color, data, and job order.
Applications: Good for small batches, samples, and projects that change designs often. It can print labels with different information on each one.
Technical Notes: Digital printing gives clear images, matches colors well, and offers many finishing choices like foil stamping and embossing. It works for food, drinks, cosmetics, and promotional labels.
Best For: Small to medium runs, lots of customization, and quick jobs.
Flexographic Printing
Flexographic printing uses flexible plates to put ink on the label material. It is a top choice for big production runs.
Definition: Flexographic printing uses flexible plates and fast presses to print labels on many materials.
Process: The press feeds rolls of material. It uses an anilox roller to add ink. The plate presses onto the material. Each color needs its own plate.
Applications: Best for printing lots of stickers, packaging, and labels on paper, plastic, foil, and cardboard.
Technical Notes: Flexo presses can print, laminate, varnish, and die-cut all at once. UV and water-based inks are common. The process supports eco-friendly packaging.
Best For: Large runs, saving money, and projects with the same design.
Offset Lithography
Offset lithography uses plates and a rubber blanket to move ink onto the label material. This method is known for sharp images.
Definition: Offset lithography prints labels by moving ink from a plate to a rubber blanket, then onto the material. It makes sharp and detailed images.
Process: The press makes high-resolution plates for each color. It uses a blanket to spread ink evenly.
Applications: Good for big, flat packages, folding cartons, and fancy labels with special finishes.
Technical Notes: Offset works with many materials, like coated paper, boards, synthetics, and special materials. It can add shiny or matte coatings for a fancy look.
Best For: Large runs, great graphics, and projects needing special finishes.
Examples | |
|---|---|
Paper Stocks | Coated, uncoated, matte |
Boards | Folding board, pearlized |
Synthetic Materials | Clear, synthetic |
Specialty Materials | Bookcloth, translucent |
Other Substrates | Metal, wood, plastic, fabric |
Gravure Printing
Gravure printing uses engraved metal cylinders to put ink on the label material. It is great for making detailed, high-quality images.
Definition: Gravure printing uses engraved cylinders filled with ink to make labels with rich colors and fine details.
Process: The press fills tiny cells on the cylinder with ink. It scrapes off extra ink. The cylinder presses onto the material.
Applications: Used for flexible food packaging, fancy labels, and very big production runs.
Technical Notes: Gravure gives bright colors, smooth fades, and steady quality for millions of prints. It works on paper, plastic films, and foils.
Best For: Very big runs, top quality, and projects with detailed graphics.
Note: Gravure costs a lot to set up but saves money for huge orders.
Screen Printing
Screen printing pushes ink through a mesh stencil onto the label material. It is liked for its toughness and special effects.
Definition: Screen printing uses a mesh screen to put thick ink layers, making labels that last in tough places.
Process: The operator makes a stencil for each color. They press ink through the screen onto the material.
Applications: Used for industrial, outdoor, medical, and safety labels that must resist water, chemicals, and sunlight.
Technical Notes: It uses special inks (metallic, bright, textured) and works on vinyl, polyester, and other synthetics. It can handle tricky designs and raised effects.
Best For: Big runs, special labels, and projects needing tough labels.
Tip: Screen printing is not good for complex, full-color designs or small batches.
Rotary Screen Printing
Rotary screen printing uses a spinning cylindrical screen to put ink as the material moves below. This method is faster and more efficient.
Definition: Rotary screen printing uses a spinning screen to print labels quickly with thick, bright ink layers.
Process: The press puts several screens around a cylinder, each for a color. As the cylinder spins, ink goes on in a steady motion.
Applications: Good for cosmetics, personal care, and labels needing strong white or raised effects.
Technical Notes: Makes bright, solid colors and textures but cannot do fine detail like digital printing. High setup costs make it best for big runs.
Best For: Fancy, tough labels in large amounts.
Aspect | Rotary Screen Printing | Traditional Flat Screen / Digital Printing |
|---|---|---|
Speed | Slower | |
Quality | Bright, solid colors | Digital: finer detail, photo effects |
Setup & Cost | High setup, efficient | Digital: faster, cheaper for small runs |
LED UV Printing
LED UV printing uses ultraviolet light to dry ink on the label surface right away. This method makes sharp, tough, and bright labels.
Definition: LED UV printing uses UV light to dry ink instantly, making labels with bright colors and strong finishes.
Process: The printer puts ink on the label. UV lamps dry it right away, so it does not smudge or bleed.
Applications: Used for beverage, food, medicine, and industrial labels, especially on materials that cannot take heat.
Technical Notes: Offers shiny or matte finishes, resists water and chemicals, and works on many materials like PE, PVC, and metal foils.
Best For: Projects needing tough labels, fast jobs, and fancy finishes.
Note: LED UV printing saves energy and is good for the environment.
Double-Sided & Peel-Back Labels
Double-sided and peel-back labels give extra space for information by using more layers or printing on both sides.
Definition: These labels have two or more layers or print on both sides, so users can peel back or see extra content.
Process: Making these labels means layering materials, printing graphics in reverse, and adding protective coatings. Special presses and glue make them strong and easy to peel.
Applications: Used for medicine, food, and labels that need extra space for instructions or legal text.
Technical Notes: Digital and flexographic printing work best for these designs, giving sharp graphics and special finishes.
Best For: Labels needing more information, legal rules, or many languages.
Thermal Printing
Thermal printing uses heat to make images on special label materials. It is a fast and reliable choice for many businesses.
Definition: Thermal printing uses heat-sensitive paper or ribbons to make labels, often for shipping, stores, and barcodes.
Process: Direct thermal printing uses heat on coated paper. Thermal transfer uses a heated ribbon to move ink onto the label.
Applications: Good for shipping labels, price tags, barcodes, and inventory stickers.
Technical Notes: Makes tough, smudge-proof labels fast. Direct thermal labels may fade over time, but thermal transfer labels last longer.
Best For: Short-term labels, shipping, and jobs needing fast, on-demand printing.
For more details, see Direct Thermal vs Thermal Transfer Labels.
Pros and Cons Overview
Digital Printing Pros
You get your labels made very fast. You can change designs often without paying extra. It works well for small and medium orders. The pictures and colors look bright and clear. You can use many kinds of materials, like paper and special films. You can print different info on each label. This is great for businesses that want quick, flexible, and nice-looking labels on many materials.
Digital Printing Cons
It can cost more for huge orders. Some special finishes are not always possible. Sometimes, colors do not match well on some materials. It is not the best for very big jobs. This works best for short runs, lots of updates, and projects with many versions.
Flexographic Pros
This method makes lots of labels fast. It is cheaper for big orders because you can use the plates again. You can use many materials, like paper, plastic, foil, and cardboard. You can add things like lamination and cutting while printing. The quality stays the same for repeat designs. This is best for big, repeat jobs with the same design.
Flexographic Cons
You need to make a plate for each design, which takes time and costs more for small jobs. It is not good for lots of design changes or small batches. The pictures may not be as sharp as digital or offset printing. It is not good for jobs that need to be done very fast or changed often. This is best for big orders with few design changes.
Offset Pros
This method makes labels with sharp, clear pictures. It saves money for big orders because each label costs less. You can use many materials, like coated paper and special boards. You can add shiny or matte finishes. The colors look the same every time. This is best for big, fancy jobs that need detailed pictures and special finishes.
Offset Cons
It takes longer to set up and costs more at first because you need plates. It is not good for small jobs or lots of design changes. It is slower than digital printing for small orders. This is best for big, high-quality jobs with the same design.
Gravure Pros
This method makes bright colors and very detailed pictures. It is good for very big orders. The labels last a long time and look the same for millions of prints. It works on paper, plastic, and metal foils. It is good for fancy packaging and luxury labels. This is best for huge jobs that need top-quality, detailed pictures.
Gravure Cons
It costs a lot to set up because you need special cylinders. It is not good for small or medium jobs. You cannot change designs often. This is best for big, long-term jobs that need high quality.
Screen Pros
This method puts thick ink on labels, so they last a long time. It works on flat, curved, or odd shapes, like glass, plastic, and metal. You can use special inks for shiny, bright, or bumpy effects. The labels can stand up to water, chemicals, and sunlight. It is good for tough, outdoor, or industrial labels. This is best for strong, special labels on hard surfaces.
Screen Cons
It is slower than other ways to make labels. It is not good for tricky, full-color designs or small orders. It costs more for short runs because of setup. This is best for big jobs that need strong labels and special effects.
Rotary Screen Pros
This way prints labels fast with thick, bright ink. The colors are strong, and you can feel raised parts. It works well for big orders and keeps the quality the same. You can add special finishes for things like makeup labels. This is best for big, bold labels with raised effects.
Rotary Screen Cons
It costs a lot to set up, so it is not good for small jobs. It cannot make tiny details like digital printing. You need skilled people to run and fix the machines. This is best for big jobs that need bold, bumpy labels.
LED UV Pros
The ink dries right away, so colors are sharp and clear. The labels can be shiny and bright and do not scratch easily. You can use many materials, even ones that soak up or do not soak up ink. It is good for the environment because it does not make bad fumes. It saves energy and works well. This is best for fast, high-quality labels that are eco-friendly.
LED UV Cons
You need special machines and skilled workers. It can cost more to start using this method. It is not always good for very thick ink. This is best for fast jobs that need to last and be good for the environment.
Double-Sided/Peel-Back Pros
These labels give you more space for info. You can add many languages, rules, or how-to steps. They work well with digital and flexographic printing for clear pictures. They are good for creative packaging and following rules. This is best for labels that need extra info or must meet rules.
Double-Sided/Peel-Back Cons
Making these labels is harder and costs more. You might need special glue and materials. They do not work for every label shape or size. This is best for jobs with strict rules or not much space.
Method Comparison
Design Complexity
How hard your design is matters when picking a printing method. Digital printing is good for tricky designs and changing info. Flexographic printing works best for simple art on big orders. Direct-to-garment printing makes sharp pictures, so it is good for fine lines. Direct-to-film printing looks nice but is not as bright as DTG. Gravure printing is great for fancy, detailed pictures on special packages. Screen and rotary screen printing make bold labels you can feel, but they do not do well with hard designs.
Run Size
How many labels you need changes the price and speed. Digital printing is best for small or medium jobs, especially if you change designs a lot. Flexographic and gravure printing save money on big orders because you can use the same plates again. Thermal printing is fast for short-term jobs like shipping or inventory. Screen and rotary screen printing are better for big batches with the same design.
Cost
Each printing method has its own costs. Digital printing is cheap to start and does not waste much, so it is good for brands with lots of products or changes. Flexographic and gravure printing cost more at first but get cheaper for big jobs. Gravure is best for making lots of fancy stickers, but following rules for the environment can cost more. Some companies use digital for small jobs and flexo or gravure for big ones.
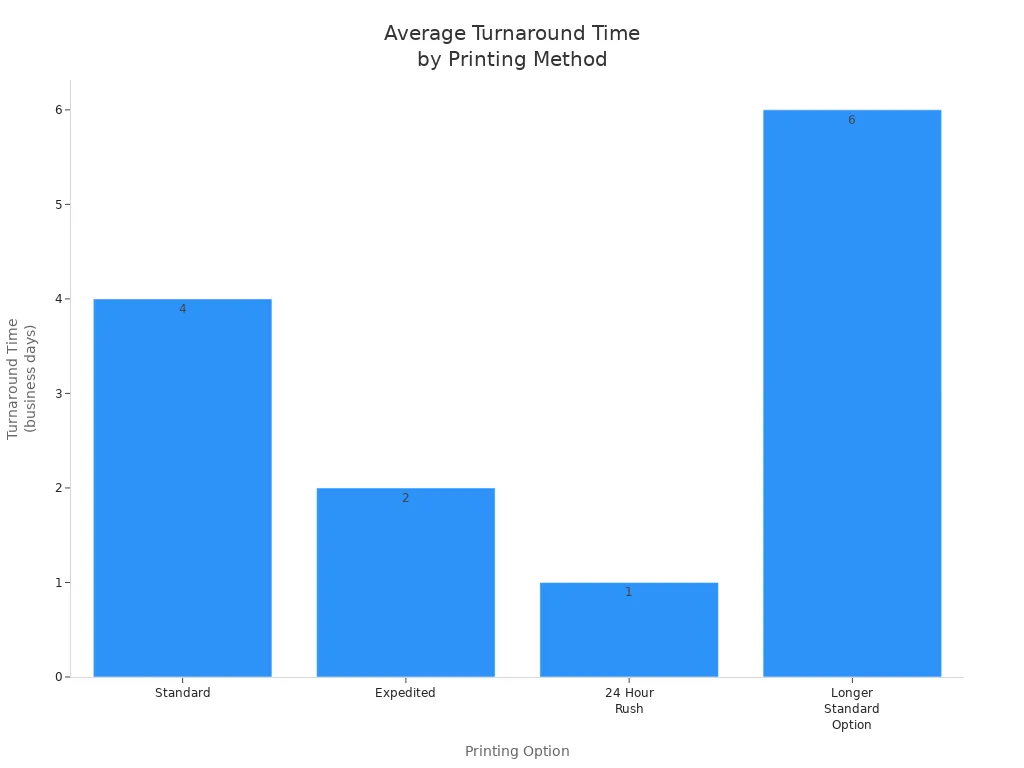
Turnaround
How fast you get your labels depends on the method and order.
Printing Option | |
|---|---|
Standard | 4 business days |
Expedited | 2 business days |
24 Hour Rush | 1 business day |
Longer Standard | 6 business days |
Substrate Options
Label printing can use many types of materials. Digital, flexographic, and offset lithography print on paper, plastic, and special materials. Gravure works on paper, plastic films, and foils. Screen and rotary screen printing are good for vinyl, polyester, and curved things. Thermal printing uses paper that reacts to heat or special ribbons.
Finishing Processes
Special finishes make labels look better and last longer. Lamination and varnish keep labels safe from water, scratches, and fading. Embossing and foil stamping make labels look and feel cool. Spot UV makes some parts shiny. Most printing methods can use these finishes, but lamination helps labels last the longest.
Summary Table: Label Printing Method Comparison
Method | Design Complexity | Run Size | Cost Efficiency | Turnaround | Substrate Options | Finishing Processes | Durability/Longevity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Digital | High | Small-Medium | High (short runs) | Fast | Paper, synthetics | Lamination, foil, embossing | Moderate |
Flexographic | Medium | Large | High (large runs) | Moderate | Paper, plastic, foil | Lamination, varnish | High |
Offset Litho | High | Large | High (large runs) | Moderate | Paper, boards, synthetics | Foil, embossing, varnish | Moderate-High |
Gravure | High | Very Large | High (mass prod.) | Slow | Paper, films, foils | Lamination, varnish | High |
Screen | Low-Medium | Large | Moderate | Slow | Vinyl, polyester | Embossing, foil, lamination | High |
Rotary Screen | Medium | Large | Moderate | Fast | Synthetics, curved | Embossing, foil, lamination | High |
LED UV | Medium | Small-Large | Moderate | Fast | PE, PVC, foils | Lamination, varnish | High |
Double-Sided/Peel-Back | Medium | Small-Large | Moderate | Moderate | Multi-layer stocks | Lamination, varnish | Moderate |
Thermal Printing | Low | Small-Medium | High (short runs) | Fast | Heat-sensitive paper | Lamination | Moderate |
Choosing a Label Printing Company
What to Look For
Picking a label printing company takes careful thought. Good companies have lots of experience in many fields. They help with labels for healthcare, food, and warehouses. They offer thermal transfer printers for strong labels that follow rules and last in tough places. A trusted company uses many printing methods, like thermal transfer and direct thermal. They make sure the printer can handle your business size.
Key things to look for are:
Label design flexibility: You can pick custom sizes, use templates, and change designs in many ways.
Barcode and QR code generation: They make many barcode types and check if they work well.
Integration capabilities: They connect with databases, spreadsheets, inventory, shipping, and online stores.
Batch printing support: They can print lots of labels at once.
Template library: You get templates for different jobs and label types.
Compliance: They follow rules like GS1-128 and can print in many languages.
Certifications and Standards: Check for FDA, ISO, or other important approvals.
Customer Support and Expertise: Their team helps you pick the best printing method and fix problems.
Tip: Ask for printed samples. This lets you see print quality, if the material works, and what finishes you can get before you choose.
Questions to Ask
When you check out a label printing company, ask questions to see if they fit your needs:
What printing methods do you have, and which one is best for my labels?
Can you show samples of work you did for my type of business?
How do you handle custom designs, changing data, and special finishes?
What certifications and standards do you meet, like FDA or ISO?
Can you connect with my inventory or shipping systems?
How fast do you finish orders?
How do you keep quality the same and follow rules?
What kind of help do you give during and after making my labels?
Looking at all these things helps you find a label printing company that gives good quality, is reliable, and uses the right technology for your labels.
Picking a custom label printing method depends on what your project needs. Every method has good and bad points. You should think about how many labels you need, your budget, your design, and the material before you choose. Knowing about these choices helps businesses get the best labels. If you want help or a price, talk to the team today.
Tip: Getting help from an expert makes sure your labels fit your brand and follow the rules.
FAQ
What is the fastest custom label printing method?
Digital printing is the quickest way to print labels. You can print straight from a computer file. This is good for rush jobs and small orders. Many businesses pick digital printing because it is fast and easy to change.
Tip: Digital printing is great if you need to fix things at the last minute.
Which printing method is best for durable outdoor labels?
Screen printing and rotary screen printing make strong labels. These labels can handle water, chemicals, and sunlight. They are good for outdoor and industrial products that need to last.
Method | Durability | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
Screen | High | Outdoor, safety |
Rotary Screen | High | Cosmetics, harsh |
Can I print different information on each label?
Digital printing lets you put new info on every label. You can change words, pictures, or barcodes for each one. This is helpful for special products, sales, or tracking items.
Note: Flexographic and offset printing do not make it easy to change info on each label.
What materials can I use for custom labels?
Label printers can use paper, plastic, vinyl, foil, and special stuff. Each printing method works with certain materials. Digital and flexographic printing can use the most types.
Paper: Coated or plain
Plastic: PE or PVC
Specialty: Foil or fabric
How do I choose the right printing method for my project?
Think about how many labels you need, your design, the material, and your budget. Digital printing is good for small, colorful jobs. Flexographic is better for big, repeat orders. Screen printing is best for strong labels. Talking to a label expert can help you pick the best way.
Tip: Ask for samples before you decide.
