
To protect thermal labels from fading or getting ruined, companies choose durable materials and reliable printing methods. This ensures barcodes and text remain clear and easy to read. Protecting thermal labels prevents costly errors and delays in retail and shipping operations. When labels fade or become unreadable, businesses risk damaging their brand reputation, increasing typing mistakes, and causing longer checkout lines. Industries such as food and healthcare rely on thermal labels to meet safety regulations. By taking steps to protect thermal labels, businesses can operate efficiently and avoid potential issues.
Key Takeaways
Pick tough thermal labels and use good printers. This helps barcodes and words stay clear and last long.
Put labels in cool, dry, and dark spots. This stops fading, curling, and glue problems.
Add laminates or coatings to shield labels. This keeps them safe from water, scratches, chemicals, and sunlight.
Be gentle when you touch labels. Try not to touch them much to stop damage and smudges.
Clean printers often and check their settings. This makes prints sharp and clear for a longer time.
Main Ways to Protect Thermal Labels
Quick Prevention Tips
You need a good plan to keep thermal labels safe. Companies can use these easy tips to help labels last longer and stay clear:
Pick strong thermal labels that can handle water, heat, and scratches. This means you do not have to replace labels often and they do not fade.
Buy good thermal printers. These printers make labels look clean and clear. This stops labels from fading and cuts down on waste.
Take care of printers and check them often. When printers work well, labels look better and you waste less.
Keep thermal labels in cool, dry, and dark places. This stops damage from the environment and keeps labels good to use.
Use labels that fit well to save material. Try eco-friendly labels like recycled or biodegradable ones.
Use smart ways to manage labels, like FIFO. This helps you use old labels first and throw away less.
Touch labels less to stop scratches and damage.
Tip: Keep labels where it is 55-85°F and 40-50% humidity. This helps labels last longer and you waste less.
Why It Matters
Thermal labels are very important in stores, shipping, and hospitals. If labels fade, barcodes can’t be read, packages get lost, and rules are broken. Picking the right label and protection plan saves money and works better. Here is a table that shows how different thermal labels compare:
Label Line | Cost Level | Protective Features | Effectiveness for Thermal Label Preservation | Suitable Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Z-Essentials | Economy | Some protective coatings; abrasion & moisture resistance | Basic protection; good for short-term or saving money | Shipping, product ID, retail pricing, work-in-process |
Z-Essentials 540T | Economy | Top-coated thermal transfer paper; permanent acrylic adhesive | Lasts well; meets FDA food rules; thinner for saving money | Shipping, food labeling, work-in-process |
Z-Perform 1000D | Mid-range entry | Uncoated direct thermal paper; permanent acrylic adhesive | Prints well; not great with water or scratches | Product ID, compliance, work-in-process, food labeling |
Z-Perform 2000D | Mid-range | Coated smooth paper; all-temp permanent acrylic adhesive | Prints better; handles weather; works in cold places | Shipping, warehousing, logistics, food packaging |
Z-Perform 2000T | Mid-range | Coated thermal transfer paper; permanent acrylic adhesive (standard and all-temp) | Prints well and lasts; meets FDA food rules; good for cold places | Packaging, product ID, compliance, work-in-process |

Thermal labels with extra layers, like coatings or laminates, can fight fading and damage from the environment. When companies protect their labels, they make fewer mistakes and people trust their brand more. These steps also help the planet by making less trash and using fewer resources. If you follow these tips, your thermal labels will last longer and work well.
Causes of Fading and Damage

Sunlight and UV
Sunlight is a big reason why thermal labels fade. Ultraviolet light can break down the label and ink. This makes the label change color and the ink fade. Over time, labels can turn yellow and get brittle. Barcodes may become hard to read. Paper-based labels fade faster than synthetic labels. Synthetic labels can handle sunlight better. Many companies use UV-resistant coatings to help protect labels from the sun.
Note: Even a short time in sunlight can make labels fade fast. This is a bigger problem for labels outside or near windows.
Heat and Humidity
Heat and humidity can also damage thermal labels. High heat makes adhesives soft. This can cause labels to curl, bubble, or peel off. Humidity adds moisture, which can make labels swell and wrinkle. Sometimes, the glue stops working. These problems can make labels change color and barcodes hard to scan. Paper labels are more likely to get damaged by heat and humidity. Synthetic labels are stronger against these problems. If the temperature changes a lot, labels can crack or pucker.
Factor | Effect on Paper-Based Labels | Effect on Synthetic Labels (e.g., Polyester) | Frequency/Contribution to Degradation |
|---|---|---|---|
Sunlight (UV) | Makes paper labels yellow, fade, and brittle; barcodes get hard to read | Synthetic labels do not yellow or crack easily; good for outdoors | Happens a lot, especially outside and with paper labels |
Heat | Makes paper dry out, curl, or lose glue; paper is weaker | Synthetic labels are stronger but glue can still get soft in heat | Happens often, depends on where the label is used |
Humidity | Makes paper swell, wrinkle, and lose glue; paper is easy to damage | Synthetic labels resist water better; some glue resists water | Happens a lot in wet or damp places |
Chemicals | Solvents and oils make paper weak and change color | Synthetic labels resist most chemicals but strong acids can hurt them | Happens often in places with lots of chemicals |
Abrasion | Paper tears, frays, and loses glue easily; barcodes wear off | Synthetic labels resist scratches better but can still get marks | Happens a lot when labels are handled or rubbed |
Chemicals and Abrasion
Chemicals and rubbing can also make labels fade and change color. Things like hand sanitizer, cleaning sprays, and oils can hurt the label’s surface. This can cause smudges, color changes, and make the glue stop working. In factories, strong cleaners and acids make labels fade even faster. Rubbing from handling, moving on belts, or touching rough things can wear away the print. This makes barcodes hard to read and damages the label more.
Common chemicals that cause fading:
Alcohol-based hand sanitizers
Cleaning sprays like acetone or bleach
Industrial oils and acids
Abrasion sources:
Staff touching labels many times
Rubbing on conveyor belts or boxes
Touching rough things or dirt
Bad print quality can also make labels fade. If the printer settings are wrong or the printhead is not set right, labels may look weak or fade fast. Taking care of printers helps keep labels clear and strong.
Label Storage

Cool, Dry, and Dark Places
Storing thermal labels the right way is important. Labels should be kept in cool, dry, and dark spots. This helps them stay clear and easy to read. It also keeps the glue strong. The best temperature is between 65°F and 75°F. Humidity should be between 40% and 55%. Keep labels in their original box or in a sealed container. This keeps out dust, water, and light.
Tip: Put desiccant packs in bins to soak up extra water. This is helpful if the air is very wet.
Humidity can cause big problems for thermal labels. If it is too wet, the glue gets weak. Labels may peel off or curl up. Too much water can also break down the coating. This makes the label change color and the print look bad. If the air is too dry, the glue dries out and does not stick well. To stop these problems, use air conditioners or dehumidifiers. Wrap labels in plastic and store them flat. This helps them keep their shape and print.
Put labels on lower shelves to keep them cool and dry.
Do not put heavy things on top of labels so they do not get squished.
Use FIFO to make sure old labels get used first.
Avoiding UV and Heat
Sunlight and heat can make labels fade fast. Direct thermal labels without a coating are very sensitive to sun and heat. Even a little sunlight can make them fade. Barcodes and words can become hard to read. Thermal transfer labels and coated labels are stronger. But all labels last longer if kept away from windows and heat.
Tests show that labels last longer in good storage. Direct thermal labels can last about a year. Thermal transfer labels can last for years if stored right. Do not put labels near machines, vents, or anything hot or wet. Use dark boxes or covers to block light and heat. This keeps labels from fading or changing color.
Note: Keeping storage the same helps labels last longer. It stops glue from failing and keeps print clear.
Prevent Thermal Labels from Fading
Choose the Right Label Type
Picking the right label type helps stop fading. Companies pick between direct thermal and thermal transfer labels. Direct thermal labels use heat-sensitive paper. This paper reacts to heat when printed. These labels are good for short-term use. But they fade fast in sunlight, heat, or chemicals. Thermal transfer labels use a ribbon to put ink on the label. These prints do not fade as easily. Thermal transfer labels last longer and handle tough places.
Synthetic labels are made from polyester, polypropylene, or vinyl. These labels are very strong. They keep water out and do not scratch easily. This makes them great for wet, dirty, or busy places. Polyester labels stay easy to read outside and at work sites. Vinyl labels can stretch and do not crack. They work well when temperatures change. BOPP labels do not get ruined by water or humidity. Freez-R-Mark™ plastic labels stick well in freezers down to -40°F.
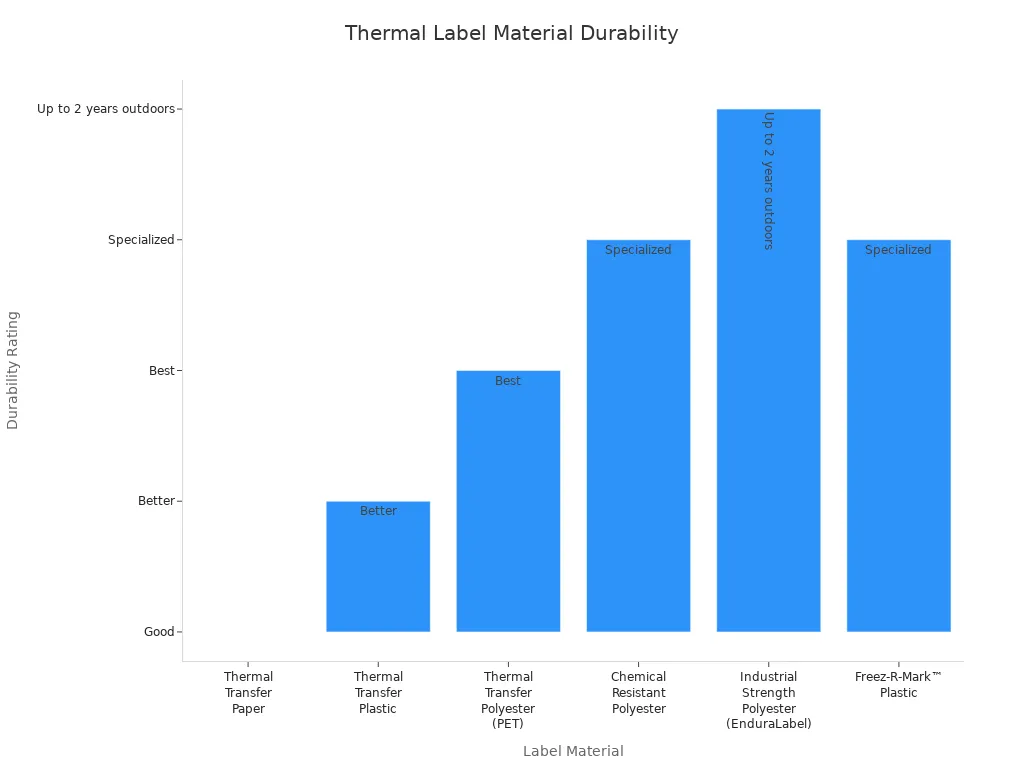
Label Material | Durability Rating | Typical Durability & Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
Thermal Transfer Paper | Good | Budget-friendly, good print quality, permanent adhesive, suitable for packaging and shipping labels. |
Thermal Transfer Plastic | Better | Resistant to water and smudging, flexible, outdoor durability 3-6 months depending on climate, used for asset tracking and product marking. |
Best | Waterproof, scratch and tear resistant, excellent durability, suitable for long-term outdoor use and harsh environments. | |
Chemical Resistant Polyester | Specialized | Waterproof, solvent and temperature resistant adhesive, ideal for chemical drums and clinical lab applications. |
Industrial Strength Polyester (EnduraLabel) | Up to 2 years outdoors | Superior adhesive for rough, oily, or textured surfaces, used in manufacturing, construction, automotive. |
Freez-R-Mark™ Plastic | Specialized | Gloss-coated plastic with freezer-grade adhesive, adheres well at freezer temperatures down to -40°F. |
Synthetic thermal labels help stop fading and color changes. Companies should pick label materials that fit their needs. Some labels work better with water, chemicals, or heat. This is a good way to keep labels from fading.
Use Laminates or Coatings
Putting laminates or coatings on labels makes them last longer. Laminates add a film layer to the label. This layer makes labels thicker and stronger. It protects labels from water, scratches, chemicals, and rough use. Polyester laminates work best for outdoor labels. They protect against rain, sun, and rubbing. Polycarbonate laminates are tough and handle high heat. They are good for machines and electronics. Polypropylene and vinyl laminates cost less and work for easy jobs.
Laminate Type | Durability Features | Suitable Applications | Cost Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
Excellent scratch and chemical resistance | Harsh environments | More expensive, may affect printer consumables | |
Polycarbonate (PC) | Outstanding impact resistance, high-temp tolerance | Extreme conditions (industrial machinery, electronics, medical) | More expensive, less cost-effective for all uses |
Polypropylene (PP) | Good chemical resistance, lightweight | Non-critical applications | Cost-effective alternative |
Vinyl (PVC) | Affordable, suitable for indoor use | Indoor applications with limited outdoor exposure | Lower cost |
Laminated thermal labels like Brother labels do not rub off or scratch easily. Tests show only small scratches after lots of rubbing. UV coatings and varnishes also help protect labels. They block sunlight and scratches but are not as strong as laminates. For a quick fix, you can use clear tape to cover labels. This simple trick helps stop fading and color changes.
Tip: Pick gloss or matte finishes for more water protection. You can also get anti-scratch or tamper-evident laminates for special needs.
Minimize Handling
Touching labels less helps stop fading and damage. If you rub or scratch labels a lot, they fade faster. Oils, water, and chemicals from hands can mark labels. This makes them hard to read. Even small scratches can make labels look bad.
Companies should teach workers not to touch labels too much. Wearing gloves keeps labels clean and safe. Using topcoated labels helps stop fading and smudging. Storing labels in cool, dry places away from sun helps them last longer. Most labels last 12-24 months. But rough use can make them last only 6 months.
Do not rub or scratch labels when putting them on.
Use machines to handle labels instead of hands.
Keep labels in closed boxes to block water and chemicals.
Put labels on clean, dry things so they stick well.
Note: Direct thermal labels are hurt by heat, light, and wet air. Handle and store labels the right way to keep them from fading and changing color.
Printer Settings and Maintenance
Calibration
Printer calibration helps keep thermal labels easy to read. When a company calibrates its printer, it changes the temperature and speed. These changes help the printer make strong prints on labels. Good calibration makes barcodes and text clear for a long time. Regular calibration also keeps labels lined up and looking the same. Companies should follow the schedule from the manufacturer. They need to calibrate when they use new label sizes or types. Adjusting speed and heat stops labels from fading or wearing out. Cleaning and aligning the printhead stops streaks and bad printing. Dust and dirt can build up inside and hurt print quality.
Tip: Calibrate the printer after big changes in label material or ribbon type to keep print quality high.
Cleaning the Printhead
Cleaning the printhead is important for good thermal labels. A dirty printhead can make streaks and faded barcodes. Companies should clean the printhead after every ribbon or label roll change. This is extra important if the printer is used a lot. Use a lint-free cloth and isopropyl alcohol to clean off dust and dirt. This keeps labels sharp and protects the printhead. A clean printhead helps the printer and labels last longer. Cleaning often stops problems that cost money to fix. Staff should not touch the printhead with their hands. They should use cleaning tools that are approved.
Ribbon and Paper Choice
Picking the right ribbon and paper is important for thermal transfer printers. The ribbon type changes how long the print lasts on labels. Companies can pick wax, wax-resin, or resin ribbons. Each ribbon has a different level of durability.
Ribbon Type | Characteristics & Use Case | Recommended Label Materials | Application Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
Wax | Cheap, prints fast, not good for tough places | Paper labels, coated and uncoated paper | Shipping labels, warehouses, short-term indoor use |
Wax/Resin | Stronger, resists chemicals, scratches, fading, and smudges | Coated paper, polypropylene, some paper labels | Barcodes, outdoor use, moderate chemical exposure |
Resin | Toughest, resists strong chemicals, heat, and scratches | Synthetic labels (polyester, vinyl, nylon) | Industrial, chemical exposure, long-term use |
Companies should match ribbon width and core size to the printer and label. They need to check if the ribbon works with their printer. Resin ribbons work best at slow speeds for top print quality. Using good ribbons and label materials stops buildup and wear. This helps thermal labels last longer.
Note: Always use ribbons and label materials that the printer manufacturer recommends for the best results.
Companies can keep thermal labels safe by doing a few things. They should store labels in cool and dry places. Picking good materials helps labels last longer. It is important to take care of printers often. These steps help stop labels from failing or getting ruined. The chart below shows how these steps lower label problems.

Check what you do now and change things that do not work. If you need help, ask a label supplier for advice. They can help you find the best choices for your business.
FAQ
What is the best way to store unused thermal labels?
Put unused thermal labels in a cool, dry, and dark spot. Keep them in their original box or a sealed container. This keeps out sunlight, heat, and water. Sunlight, heat, and moisture can make labels fade or lose their stick.
How can someone prevent thermal labels from fading quickly?
Pick the right label type for where you use it. Add laminates or coatings for more protection. Try not to touch labels too much. Store labels away from sunlight and heat. Clean and check printers often to keep prints looking good.
Which chemicals damage thermal labels the most?
Alcohol hand sanitizers, acetone, bleach, and industrial oils can hurt thermal labels. These chemicals can make labels fade, smudge, or lose their stick. Keep labels away from strong cleaning products.
Why do some thermal labels look faded right after printing?
Bad print quality can happen if printer settings are wrong. A dirty printhead or using the wrong ribbon or label can also cause fading. Calibrate and clean printers often to keep prints clear and strong.
Can someone use clear tape to protect a thermal label?
Yes, clear packing tape can quickly protect labels from water, scratches, and light. For longer-lasting protection, use professional laminates or coatings. These work better than tape over time.
