
Many people confuse 2D barcodes vs QR codes, but they are not the same. A QR code is just one type of two-dimensional barcode, while not every 2D barcode qualifies as a QR code. It’s important for businesses and tech leaders to understand the distinction between 2D barcodes vs QR codes. The use of QR codes is rapidly growing worldwide, with projections showing that by 2025, QR code scans could exceed 41 million—a 433% increase.
Understanding the differences between 2D barcodes vs QR codes helps organizations choose the most suitable barcode for their specific needs.
Key Takeaways
QR codes are a kind of 2D barcode. They have a square shape and three marks in the corners. This makes them easy to scan with smartphones.
Other 2D barcodes like Data Matrix, PDF417, and Aztec have special uses. They help track small things or are used in factories and airports.
2D barcodes can hold more data than 1D barcodes. They still work if they are a little damaged because of error correction.
Picking the right barcode depends on your data needs. It also depends on where you use it and how you scan and use the code.
QR codes are good for daily things like ads and payments. Other 2D barcodes are better for factories and safe tracking jobs.
2D Barcodes vs QR Codes

Key Differences
When you look at 2d barcodes and qr codes, you see some big differences. Both are part of the barcode family. But they do not look or work the same way.
QR codes are one kind of 2d barcode. They have a square shape with three big marks in the corners. There are also many small black and white squares. This design helps people scan them quickly from any direction.
Other 2d barcodes, like Data Matrix, PDF417, and Aztec, look different. Data Matrix codes are small and fit on tiny things. PDF417 uses lines stacked on top of each other. You often see these on papers. Aztec codes have a bullseye in the middle. They work well for tickets on phones.
QR codes can hold both static and dynamic data. This means you can change the info without making a new code. Other 2d barcodes are good for holding lots of data in a small space. This is helpful for factories or special jobs.
The way these barcodes store data is not the same. QR codes use black and white squares. Data Matrix uses dots. Aztec has a bullseye. PDF417 uses stacked lines. These differences change how scanners read them.
Error correction is also important. QR codes can fix mistakes up to 30%. Data Matrix can fix up to 33%. PDF417 and Aztec also have strong error correction. Sometimes you can change how much they correct.
Barcode Type | Structure & Visuals | Error Correction | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
QR Code | Square grid, 3 position markers | Marketing, payments, ticketing | |
Data Matrix | Compact dots, square/rectangular | Up to 33% | Medical devices, electronics |
PDF417 | Stacked linear bars | Robust | Documents, ID cards |
Aztec | Bullseye center, no quiet zone needed | Robust | Mobile tickets, transport |
Note: QR codes are made for fast scanning and work with most smartphones. Other 2d barcodes are often used for special jobs or in factories.
Why It Matters
Knowing the differences between 2d barcodes and qr codes helps companies make smart choices. The barcode you pick changes how much data you can store, how you scan it, and how safe it is.
QR codes are great for things people use every day. They are easy to scan and read fast. This makes them good for ads, paying with your phone, or linking to websites.
Other 2d barcodes, like Data Matrix and PDF417, are used for special jobs. They are best when you have little space or need to store lots of info, like in hospitals or factories.
In supply chains, QR codes with GS1 Digital Link can be used as store barcodes and digital links. But companies must follow GS1 rules when making these codes.
Security is different for each barcode. QR codes can have passwords or be locked, but sometimes people use them in bad ways. Other 2d barcodes are simpler but can be made safer with software.
It is important for growing companies to think about how barcodes fit with their systems. QR codes work well with apps and can grow with your business. Other 2d barcodes help track products and manage data in supply chains.
Aspect | QR Codes | Other 2D Barcodes (e.g., GS1 Digital Link) |
|---|---|---|
High; supports multimedia and URLs | Complex data (GTIN, batch, expiry) | |
Scanning Technology | Smartphone-friendly | Often needs specialized scanners |
Security Features | Advanced options, but risk of misuse | Simpler, can be enhanced with software |
Intended Use Cases | Marketing, payments, digital engagement | Asset tracking, inventory, supply chain |
Standards & Compliance | Open design, may not meet all GS1 standards | Must follow GS1 guidelines |
Companies should pick the barcode that fits their needs and rules. The right barcode helps you read data easily, keep info safe, and work well with your systems.
1D and 2D Barcodes
Structure
A barcode helps people and machines get info fast. 1D barcodes use lines and spaces that go side to side. The lines and spaces are different sizes. This is how they hold information. 2D barcodes use a grid or matrix. They have dots, squares, or shapes in patterns. These patterns hold info across and up and down. This makes 2D barcodes smaller and stronger.
1D barcodes need more room because they only go one way.
2D barcodes can hold more info in less space.
1D barcodes do not fix mistakes well. If they get damaged, they are hard to scan.
2D barcodes can fix mistakes better. They still work if part is missing.
1D barcodes need laser scanners. 2D barcodes work with cameras or phones.
Studies show 2D barcodes work better in tough places. Their design helps them get read even if scratched or dirty.
Data Capacity
How much info a barcode holds depends on its design. 1D barcodes usually hold less than 100 letters or numbers. Most, like Code 39, hold about 20 to 23. Code 128 can hold up to 80. 2D barcodes can hold thousands of letters or numbers. QR codes can hold up to 4,296. Data Matrix codes hold about 1,500. Some, like Han Xin Code, can hold over 4,000.
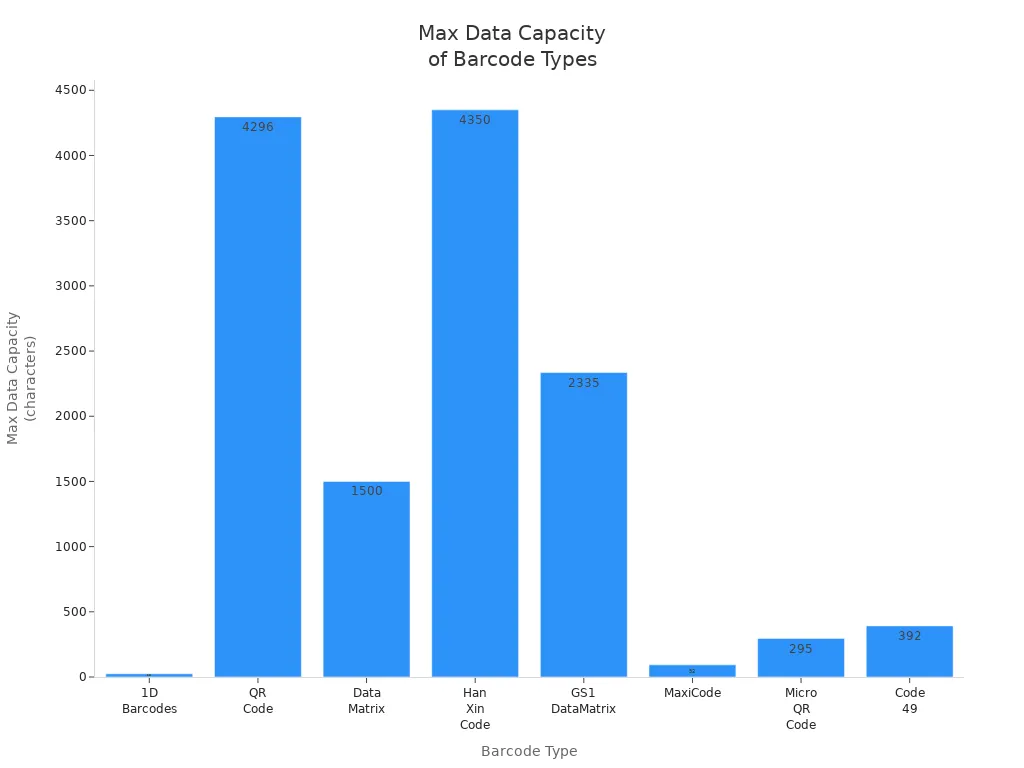
Barcode Type | Maximum Data Capacity |
|---|---|
1D Barcodes | Less than 100 characters |
QR Code | Up to 4,296 characters |
Data Matrix | About 1,500 characters |
Han Xin Code | Over 4,000 characters |
Because 2D barcodes hold more info, people use them in new ways. They can show product details, batch numbers, and when things expire. 2D barcodes can also link to websites and digital stuff. They are easy to scan, even with lots of info. Scanning is quick and works well. Many businesses use 2D barcodes for tracking, rules, and talking to customers. Their strong design and error fixing make 2D barcodes great for today’s needs.
Types of 2D Barcodes
QR Codes
QR codes are the most common 2D barcode people see. They are square and have three big marks in the corners. This shape lets you scan them fast from any side. QR codes can still be read if they get damaged because they fix mistakes well. People use QR codes for ads, paying with phones, menus, and tickets. You can scan them with a smartphone. They can link to videos or websites. You can also add logos or colors to make them look special. These things make QR codes popular in stores, hospitals, and shows. QR codes help people learn about products, keep track of items, and talk to customers.
QR codes are part of the 2D barcode group. They are very flexible and work with almost any phone. They can hold more info than barcodes and are easy to scan.
Data Matrix
Data Matrix barcodes are made of tiny black and white squares in a grid. They can hold lots of info in a small spot. This makes them good for tiny things like chips, medical tools, and medicine. They do not break easily and can be read even if scratched. Data Matrix codes can show batch numbers and when things expire. This helps people follow items in the supply chain. Their small size and strong design are best for places where space and toughness are important.
PDF417
PDF417 barcodes look like rows of lines stacked on top of each other. They can hold more info than most barcodes. They can store words, numbers, and even files. Airlines use them for boarding passes and bags. Governments put them on ID cards and driver’s licenses. Warehouses use them to keep track of things. PDF417 barcodes can hold lots of data and can show hard info. They help move things faster in travel, hospitals, and shipping by storing lots of details and scanning quickly.
Aztec
Aztec barcodes have a bullseye shape in the middle. They do not need extra space around them, so they fit on small tickets and papers. Aztec codes can hold lots of travel and passenger info. This makes them good for train and plane tickets. They can be scanned fast and work even if part is missing. Aztec barcodes are easy to read, save space, and do not break easily. These things help make ticketing safe and quick for travelers.
QR codes are easier to use than barcodes and other 2D types. They are good for getting people involved and work with many devices. QR codes are the most flexible, but each 2D barcode is best for different jobs.
Differences in Applications
Business Uses
Businesses pick barcode types for their own needs. QR codes are very flexible and work well for customers. Companies use QR codes in ads, events, healthcare, and tracking items. These codes can link to websites, social media, Wi-Fi, and tickets. QR codes also make paying easy by letting people pay with their phones. You do not need special tools to use them.
Other 2D barcodes, like Data Matrix, PDF417, and Aztec, have special jobs. Data Matrix codes help factories mark small parts and track medical tools. PDF417 barcodes hold lots of shipping and batch info. They are good for shipping and ID cards. Aztec codes are great for tickets and fast scanning at airports.
Many businesses pick QR codes because they are easy to scan with phones. You can also change what they show fast. Other 2D barcodes are better for factories and shipping. They are strong and can hold lots of info.
Industry Examples
Different jobs use special barcode labels to work better. In shipping, companies like DHL, UPS, and Amazon use QR codes on boxes. This helps track packages and manage stock in real time. These barcodes cut down on mistakes and make things faster. They also let people see where their package is.
Barcode Type | Industry | Application Example |
|---|---|---|
QR Code | Logistics, Retail | Tracking packages, updating stock, talking to customers |
Data Matrix | Manufacturing, Healthcare | Marking chips, tracking medical tools, managing batches |
PDF417 | Shipping, Government | Shipping labels, ID cards, medical records |
Aztec | Airline, Inventory | Boarding passes, mobile tickets, fast scanning in inventory systems |
Factories use Data Matrix and PDF417 barcodes to track parts and keep stock. Hospitals use Data Matrix codes to track medical tools and keep patients safe. Airlines use Aztec codes for boarding passes. These codes scan fast, even if the print is not perfect.
Security and how barcodes work are not the same. QR codes fix mistakes well and work with most phones. But sometimes people can change them or steal info. Companies can use digital locks to keep QR code data safe. Other 2D barcodes are tough and fix mistakes too. They are good for hard jobs in factories.
Picking the right barcode helps each job be faster, safer, and more correct. Companies should use the barcode that fits their needs best.
Choosing the Right Barcode
Data Needs
Picking the right barcode starts with knowing your data needs. Each barcode can hold a different amount of info. 1D barcodes are good for simple jobs. They store basic numbers or letters. If you need to store more info, use a 2D barcode. QR codes and Data Matrix can hold thousands of characters. These are great for healthcare, stores, and shipping. The kind of info you need to store helps you choose. If you track products with batch numbers or dates, use a 2D barcode. QR codes and PDF417 have error correction. This means they still work if damaged. Think about the future too. As your business grows, you may need to store more info. Pick a barcode that can handle more data. This helps your system work well for a long time.
Tip: Make sure the barcode can hold all the info you need. This helps you avoid scanning mistakes and slowdowns.
Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
How much info the code can hold; each type is different. | |
Application specifics | Rules or needs for your job or industry. |
Future scalability | Can the code handle more info if you need it later? |
Compatibility with data processing systems | How easy it is to use with your current inventory system. |
Environment
Where you use the barcode matters a lot. Light, the surface, and barcode quality all change how well it scans. Bad lighting or shiny surfaces make scanning hard. Dust, water, and scratches can hurt the barcode. This can cause mistakes when tracking items. 2D barcodes like QR codes and Data Matrix have error correction. They still work if part of the code is missing. In tough places, companies use strong labels like polyester or UV ink. These keep the barcode safe from rain, chemicals, and heat. In warehouses or outside, 2D barcodes on strong labels last longer than 1D barcodes.
Environmental Factor | Effect on Barcode Performance |
|---|---|
Too much or too little light makes scanning harder. | |
Surface Texture & Material | Shiny or curved surfaces make codes harder to read. |
Barcode Quality | Dirt, water, and scratches make scanning worse and cause mistakes. |
Temperature & Humidity | Very hot, cold, or wet places can damage barcodes and mess up tracking. |
Durability | Stronger labels help barcodes last longer and work better in tough places. |
Note: For outdoor or factory jobs, pick a barcode and label that are made to last and work well.
Businesses need to know that QR codes can hold a lot of data. They scan fast and work with most smartphones. Other 2D barcodes, like Data Matrix and PDF417, are small and good for factories.
Feature | QR Code | Other 2D Barcodes (Data Matrix, PDF417, Aztec) |
|---|---|---|
Data Capacity | Varies by type | |
Error Correction | High (up to 30%) | Moderate to high |
Compatibility | Universal (smartphones, scanners) | Some need special scanners |
Customization | Supports branding | Less flexible |
To pick the best barcode, companies should do these steps. First, know what you want the barcode to do. Next, think about what you are tracking and how it moves. Then, make sure the barcode is easy to read. After that, check if your scanner works with the barcode. Last, look at the rules for your industry.
If you want to learn more, you can use guides from GS1, HowStuffWorks, and Keyence. These guides help you understand barcode technology and new trends.
